Two special methods for treating insomnia
By Jason 11 Mar,2024
What constitutes insomnia?
Insomnia is generally defined by the following symptoms: taking longer than 30 minutes to fall asleep; waking up more than 3 times per night or experiencing early morning awakenings; having shallow or vivid dreams during sleep; sleeping for less than 6 hours per night accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, mental fatigue, excessive sleepiness, and lethargy the next day.
Medication therapy, physical therapy, cognitive therapy, including behavioral therapy, are all commonly used.
There is no single method that can perfectly solve the problem of insomnia. Often, a combination of therapies is necessary.
OTHER NEWS
-
- Should I continue brushing if my gums bleed?
- By Dr. James 21 Mar,2024
-
- Eating these foods can help bone fracture patients recover their health
- By Jason 05 Mar,2024
-
- How to relieve migraine after tooth extraction and its causes
- By Jason 14 Mar,2024

-
- The cause of abdominal bowel sounds
- By Jason 05 Mar,2024

-
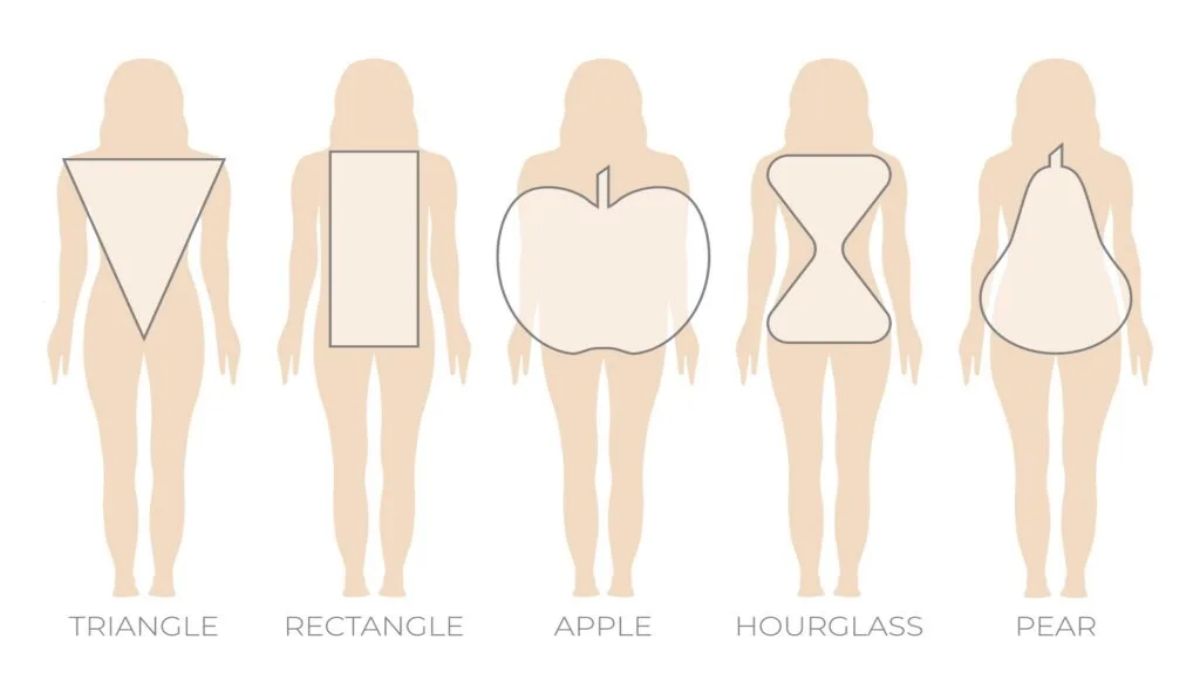
- SUMMER DRESSES FOR DIFFERENT BODY TYPES
- By Fatima Amir 08 May,2024
-
- 5 Non-surgical Beauty Treatments for Better Skin
- By Fatima Amir 07 May,2024
-
- 6 Yoga Postures for Staying Fit in your 60s
- By Fatima Amir 17 May,2024

-
- How to Alleviate Lower Back Pain Through Diet
- By Jason 05 Mar,2024

-
- Life Insurance for Different Life Stages_ What to Consider.docx
- By Prodosh Kundu 14 Aug,2024

-
- Possible causes of facial swelling
- By Jason 06 Mar,2024

-
- Questions to Ask your Doctor after Menopause and Health Chechups
- By Fatima Amir 23 May,2024

-
- Things You Need to Know About Gum Bleeding
- By Dr. James 21 Mar,2024

 1
1 1
1